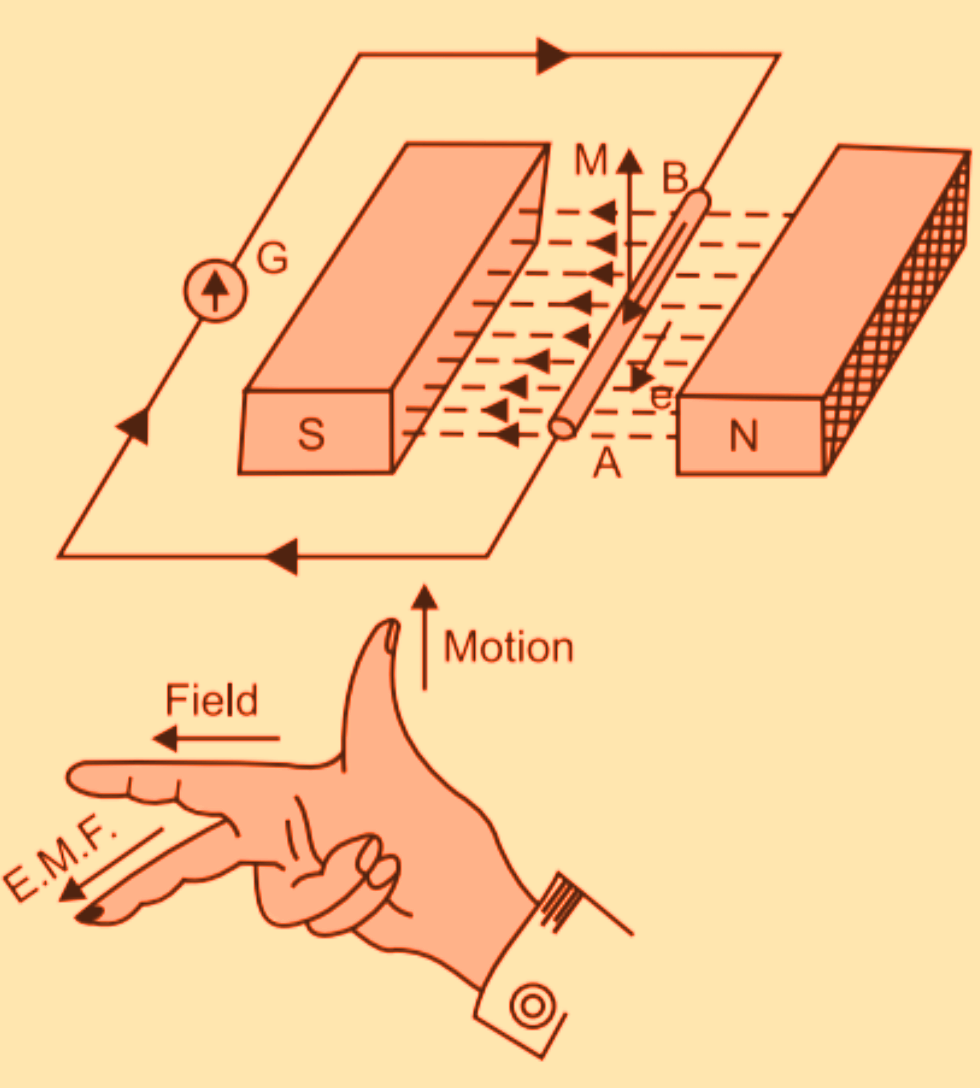
Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force . A special type of potential difference is known as electromotive force (emf). It is a special type of potential difference. emf is not a force at all; we learned the relationship between induced electromotive force (emf) and magnetic flux. To be precise, the electromotive force (emf) is the potential difference of a source when no current is flowing. all such devices create a potential difference and can supply current if connected to a circuit. In a nutshell, the law states that changing. electromotive force is defined as the electric potential produced by either an electrochemical cell or by changing the magnetic field. in electromagnetism and electronics, electromotive force or emf (measured in volts) is the electrical action produced by. calculate induced electromotive force and current. The emf is not a force at all, but the term ‘electromotive force’ is used for historical reasons. electromotive force (emf) and potential difference are both measured in volts but signify distinctly different concepts. Units of emf are volts.
from animalia-life.club
in electromagnetism and electronics, electromotive force or emf (measured in volts) is the electrical action produced by. emf is not a force at all; all such devices create a potential difference and can supply current if connected to a circuit. electromotive force (emf) and potential difference are both measured in volts but signify distinctly different concepts. Units of emf are volts. To be precise, the electromotive force (emf) is the potential difference of a source when no current is flowing. In a nutshell, the law states that changing. It is a special type of potential difference. calculate induced electromotive force and current. we learned the relationship between induced electromotive force (emf) and magnetic flux.
Faradays Law Of Induction Equation
Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force To be precise, the electromotive force (emf) is the potential difference of a source when no current is flowing. in electromagnetism and electronics, electromotive force or emf (measured in volts) is the electrical action produced by. electromotive force (emf) and potential difference are both measured in volts but signify distinctly different concepts. all such devices create a potential difference and can supply current if connected to a circuit. electromotive force is defined as the electric potential produced by either an electrochemical cell or by changing the magnetic field. we learned the relationship between induced electromotive force (emf) and magnetic flux. calculate induced electromotive force and current. Units of emf are volts. It is a special type of potential difference. The emf is not a force at all, but the term ‘electromotive force’ is used for historical reasons. In a nutshell, the law states that changing. emf is not a force at all; A special type of potential difference is known as electromotive force (emf). To be precise, the electromotive force (emf) is the potential difference of a source when no current is flowing.
From www.sciencefacts.net
& Force Definition & Eqn. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force Units of emf are volts. electromotive force is defined as the electric potential produced by either an electrochemical cell or by changing the magnetic field. in electromagnetism and electronics, electromotive force or emf (measured in volts) is the electrical action produced by. To be precise, the electromotive force (emf) is the potential difference of a source when no. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From kremilasg.blogspot.com
What Is Electromotive Force Emf Vs Pd Physics Classroom Learn Physics Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force in electromagnetism and electronics, electromotive force or emf (measured in volts) is the electrical action produced by. In a nutshell, the law states that changing. To be precise, the electromotive force (emf) is the potential difference of a source when no current is flowing. The emf is not a force at all, but the term ‘electromotive force’ is used. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From exoagwlbh.blob.core.windows.net
Field And Electric Current at Nicky Dille blog Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force electromotive force is defined as the electric potential produced by either an electrochemical cell or by changing the magnetic field. electromotive force (emf) and potential difference are both measured in volts but signify distinctly different concepts. in electromagnetism and electronics, electromotive force or emf (measured in volts) is the electrical action produced by. To be precise, the. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Faraday’s Law of Induction Lenz’s Law Physics Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force electromotive force is defined as the electric potential produced by either an electrochemical cell or by changing the magnetic field. Units of emf are volts. It is a special type of potential difference. we learned the relationship between induced electromotive force (emf) and magnetic flux. electromotive force (emf) and potential difference are both measured in volts but. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From circuitglobe.com
What is EMF (Electromotive Force) ? Circuit Globe Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force To be precise, the electromotive force (emf) is the potential difference of a source when no current is flowing. The emf is not a force at all, but the term ‘electromotive force’ is used for historical reasons. A special type of potential difference is known as electromotive force (emf). calculate induced electromotive force and current. emf is not. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From mmerevise.co.uk
Induction Questions and Revision MME Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force Units of emf are volts. In a nutshell, the law states that changing. The emf is not a force at all, but the term ‘electromotive force’ is used for historical reasons. It is a special type of potential difference. A special type of potential difference is known as electromotive force (emf). all such devices create a potential difference and. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From sdsu-physics.org
Faradays Law Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force we learned the relationship between induced electromotive force (emf) and magnetic flux. In a nutshell, the law states that changing. Units of emf are volts. calculate induced electromotive force and current. electromotive force (emf) and potential difference are both measured in volts but signify distinctly different concepts. The emf is not a force at all, but the. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From eevibes.com
what is the difference between electromotive force and potential Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force in electromagnetism and electronics, electromotive force or emf (measured in volts) is the electrical action produced by. In a nutshell, the law states that changing. To be precise, the electromotive force (emf) is the potential difference of a source when no current is flowing. It is a special type of potential difference. electromotive force (emf) and potential difference. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From www.pinterest.com
Faraday's law of induction vector illustration Electromotive force Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force we learned the relationship between induced electromotive force (emf) and magnetic flux. A special type of potential difference is known as electromotive force (emf). To be precise, the electromotive force (emf) is the potential difference of a source when no current is flowing. In a nutshell, the law states that changing. electromotive force is defined as the electric. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From www.thesciencehive.co.uk
Induction (GCSE) — the science sauce Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force electromotive force is defined as the electric potential produced by either an electrochemical cell or by changing the magnetic field. In a nutshell, the law states that changing. It is a special type of potential difference. Units of emf are volts. all such devices create a potential difference and can supply current if connected to a circuit. . Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT and Electromotive Force PowerPoint Presentation, free Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force To be precise, the electromotive force (emf) is the potential difference of a source when no current is flowing. emf is not a force at all; we learned the relationship between induced electromotive force (emf) and magnetic flux. The emf is not a force at all, but the term ‘electromotive force’ is used for historical reasons. electromotive. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Fields Chapter 29 (continued) PowerPoint Presentation Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force A special type of potential difference is known as electromotive force (emf). To be precise, the electromotive force (emf) is the potential difference of a source when no current is flowing. we learned the relationship between induced electromotive force (emf) and magnetic flux. all such devices create a potential difference and can supply current if connected to a. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From www.vrogue.co
Fields Inside Perfec vrogue.co Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force electromotive force is defined as the electric potential produced by either an electrochemical cell or by changing the magnetic field. in electromagnetism and electronics, electromotive force or emf (measured in volts) is the electrical action produced by. electromotive force (emf) and potential difference are both measured in volts but signify distinctly different concepts. calculate induced electromotive. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From www.tutoroot.com
Force Guide 2024 Definition, Diagrams Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force in electromagnetism and electronics, electromotive force or emf (measured in volts) is the electrical action produced by. The emf is not a force at all, but the term ‘electromotive force’ is used for historical reasons. calculate induced electromotive force and current. A special type of potential difference is known as electromotive force (emf). emf is not a. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From animalia-life.club
Faradays Law Of Induction Equation Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force we learned the relationship between induced electromotive force (emf) and magnetic flux. calculate induced electromotive force and current. It is a special type of potential difference. all such devices create a potential difference and can supply current if connected to a circuit. The emf is not a force at all, but the term ‘electromotive force’ is used. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From www.pinterest.co.uk
Scientific Field and vector illustration Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force Units of emf are volts. emf is not a force at all; A special type of potential difference is known as electromotive force (emf). electromotive force is defined as the electric potential produced by either an electrochemical cell or by changing the magnetic field. electromotive force (emf) and potential difference are both measured in volts but signify. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From universe.nasa.gov
Forces Universe NASA Universe Exploration Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force A special type of potential difference is known as electromotive force (emf). It is a special type of potential difference. electromotive force (emf) and potential difference are both measured in volts but signify distinctly different concepts. electromotive force is defined as the electric potential produced by either an electrochemical cell or by changing the magnetic field. calculate. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.
From www.sciencefacts.net
& Force Definition & Eqn. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force Units of emf are volts. in electromagnetism and electronics, electromotive force or emf (measured in volts) is the electrical action produced by. The emf is not a force at all, but the term ‘electromotive force’ is used for historical reasons. electromotive force is defined as the electric potential produced by either an electrochemical cell or by changing the. Electromagnetic Field Vs Electromotive Force.